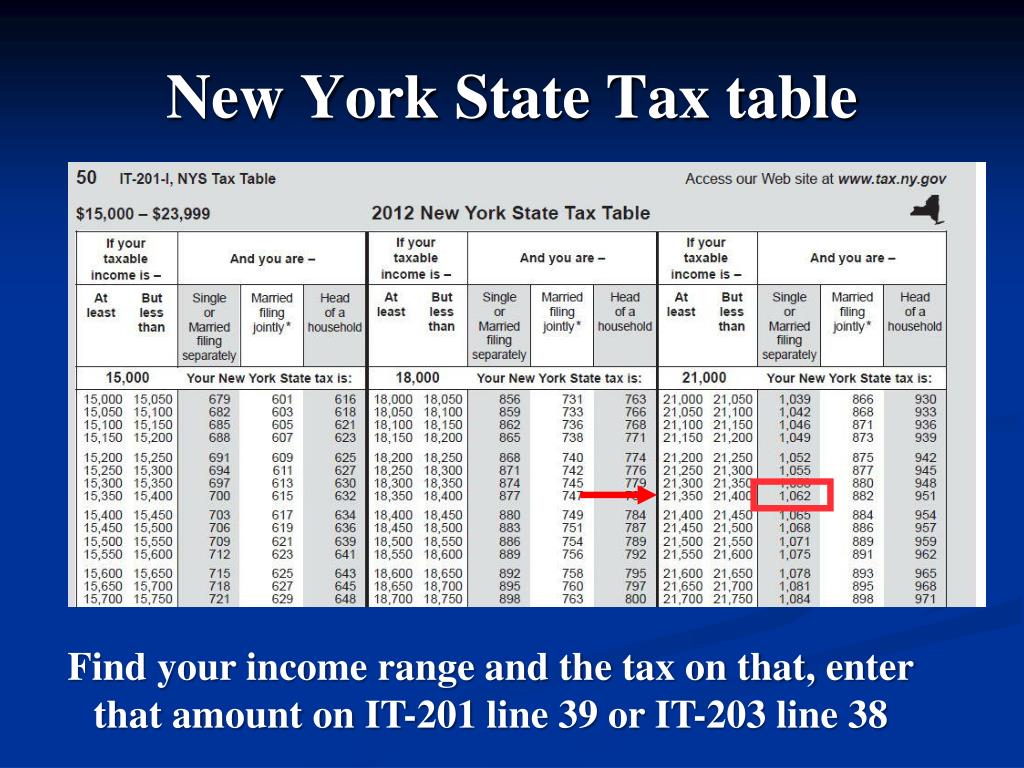
When it comes to managing finances, understanding NYC state income tax is crucial for anyone living or working in the city. New York City residents face a unique tax structure that combines both state and local taxes, making it one of the most complex tax systems in the United States. Whether you're a new resident, a small business owner, or someone who's been in the city for years, navigating this intricate system can be overwhelming. This article will break down everything you need to know about NYC state income tax, offering insights into how it works, who it affects, and how to ensure compliance while maximizing your deductions.
The importance of staying informed about NYC state income tax cannot be overstated. With ever-changing regulations and frequent updates, keeping up with the latest tax laws is essential to avoid penalties and optimize your financial health. The tax burden in New York City is among the highest in the nation, which means understanding your obligations and rights is critical. From filing deadlines to deductions, exemptions, and credits, this guide will provide a detailed overview to help simplify the process and make tax season less daunting.
Whether you're a young professional, a family looking to settle down in the city, or a retiree planning your finances, this article aims to answer all your questions. By the end of this piece, you'll have a clear understanding of how NYC state income tax works, what factors influence your tax rate, and how to navigate the complexities of the system. Let's dive in and explore everything you need to know to stay compliant and financially savvy.
Read also:Toms Forklift Certification And Training Your Ultimate Guide To Mastering The Machine
Table of Contents
- 1. What Is NYC State Income Tax?
- 2. How Is NYC State Income Tax Calculated?
- 3. Who Pays NYC State Income Tax?
- 4. How Can You Reduce Your NYC State Income Tax?
- 5. Why Are NYC State Income Tax Rates So High?
- 6. What Are the Deadlines for NYC State Income Tax Filing?
- 7. How Does NYC State Income Tax Impact Retirees?
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions About NYC State Income Tax
What Is NYC State Income Tax?
NYC state income tax refers to the taxes levied by the State of New York on the income earned by individuals, businesses, and other entities residing or operating within its borders. This tax is a critical source of revenue for the state government, funding public services such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and public safety. Unlike federal income tax, which is uniform across the United States, NYC state income tax has its own set of rules, rates, and regulations tailored to the specific needs of the state.
One of the unique aspects of NYC state income tax is the additional local tax imposed by the city of New York. This means that residents of the city not only pay state income tax but also an additional municipal tax, further increasing their overall tax burden. The combination of state and local taxes makes New York City one of the highest-taxed metropolitan areas in the country.
In addition to individual taxpayers, businesses operating in New York City are also subject to NYC state income tax. Corporations, partnerships, and other business entities must file separate tax returns and pay taxes on their profits. The complexity of the system requires businesses to stay informed about the latest tax laws and regulations to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
How Does NYC State Income Tax Differ From Federal Income Tax?
While both NYC state income tax and federal income tax aim to generate revenue, they differ significantly in terms of rates, exemptions, and deductions. The federal government uses a progressive tax system, where higher-income earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes. NYC state income tax, on the other hand, follows a similar progressive structure but with its own set of brackets and rates.
Furthermore, NYC state income tax allows for certain deductions and credits that are not available at the federal level. For example, New York State offers a deduction for contributions to a 529 college savings plan, which can help reduce your taxable income. Understanding these differences is essential for maximizing your deductions and minimizing your tax liability.
Key Features of NYC State Income Tax
- Progressive tax rates based on income levels
- Additional local tax for NYC residents
- Unique deductions and credits available only in New York State
- Annual filing requirements for individuals and businesses
How Is NYC State Income Tax Calculated?
Calculating NYC state income tax involves several steps, starting with determining your taxable income. This is done by subtracting allowable deductions and exemptions from your gross income. Once you have your taxable income, you can apply the appropriate tax rate based on your filing status and income bracket.
Read also:How To Report Fake Facebook Accounts A Comprehensive Guide
NYC state income tax uses a progressive tax system, meaning that higher-income earners pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes. The state has several tax brackets, each with its own rate. For example, as of 2023, the lowest bracket is taxed at 4%, while the highest bracket is taxed at 8.82%. These rates are subject to change, so it's important to stay updated on the latest tax laws.
In addition to state income tax, NYC residents must also calculate and pay local income tax. This is done separately but follows a similar process. The local tax rate is generally lower than the state rate but still adds to the overall tax burden. To simplify the process, many taxpayers use tax software or consult with a tax professional to ensure accurate calculations and compliance.
What Factors Influence NYC State Income Tax Rates?
Several factors can influence your NYC state income tax rate, including your filing status, income level, and any applicable deductions or credits. For example, individuals filing as single may have a different tax rate than those filing jointly with a spouse. Similarly, taxpayers with dependents or specific expenses, such as mortgage interest or charitable donations, may qualify for additional deductions or credits that can lower their tax liability.
Another important factor is the location of your income. If you work in New York City but reside in a neighboring state, you may still be subject to NYC state income tax on the income earned within the city. This is known as the "convenience of the employer" rule and can complicate tax filings for commuters.
Steps to Calculate NYC State Income Tax
- Determine your gross income
- Subtract allowable deductions and exemptions
- Apply the appropriate tax rate based on your income bracket
- Add any applicable local taxes
- Review for available deductions and credits
Who Pays NYC State Income Tax?
NYC state income tax applies to a wide range of individuals and entities, including residents, non-residents, and businesses. Residents of New York State, including those living in New York City, are required to pay state income tax on all their income, regardless of where it was earned. Non-residents who earn income within the state, such as commuters or contractors, are also subject to NYC state income tax on the income earned within the state.
Businesses operating in New York City, whether they are corporations, partnerships, or sole proprietorships, must also pay NYC state income tax on their profits. The tax obligations for businesses can vary depending on their structure, size, and location. For example, corporations are subject to a flat tax rate, while partnerships and sole proprietorships may pass through their income to the owners, who then pay individual income tax.
It's important to note that certain groups, such as retirees and low-income individuals, may qualify for exemptions or reduced tax rates. Understanding these exemptions and how they apply to your situation can help you minimize your tax liability.
Do Retirees Pay NYC State Income Tax?
Retirees living in New York City are generally subject to NYC state income tax, but there are certain exemptions and deductions available to them. For example, New York State offers a retirement income exclusion that allows retirees to exclude a portion of their pension, annuity, or retirement plan income from taxation. Additionally, Social Security benefits are not subject to NYC state income tax, providing some relief for retirees on fixed incomes.
However, retirees with other sources of income, such as rental income or investment gains, may still be subject to NYC state income tax on those earnings. It's crucial for retirees to carefully review their tax situation and consult with a tax professional if needed to ensure they are taking full advantage of available exemptions and deductions.
How Can You Reduce Your NYC State Income Tax?
Reducing your NYC state income tax liability involves strategically utilizing available deductions, credits, and exemptions. One of the most effective ways to lower your tax burden is by maximizing your contributions to retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s or IRAs. Contributions to these accounts are typically tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income for the year.
Another option is to take advantage of education-related deductions, such as the 529 college savings plan deduction mentioned earlier. Contributions to a 529 plan can be deducted from your state taxable income, up to a certain limit, helping you save for future education expenses while reducing your tax liability.
Additionally, consider itemizing your deductions if your total itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction. This can include expenses such as mortgage interest, property taxes, and charitable contributions. While itemizing requires more effort, it can result in significant tax savings for those with substantial deductions.
What Credits Are Available to Reduce NYC State Income Tax?
NYC state income tax offers several credits that can help reduce your tax liability. One of the most popular is the Child Tax Credit, which provides a credit for each qualifying child under the age of 17. This credit can significantly lower your tax bill, especially for families with multiple children.
Another valuable credit is the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), which is designed to benefit low- to moderate-income working individuals and families. The EITC can result in a refundable credit, meaning you may receive a refund even if you owe no taxes.
Credit Examples
- Child Tax Credit
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
- Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP) Credit
Why Are NYC State Income Tax Rates So High?
The high NYC state income tax rates are primarily due to the significant expenses incurred by the state and city governments. New York City, in particular, faces substantial costs related to maintaining its extensive public transportation system, funding public schools, and supporting a wide range of social services. These expenses require a steady stream of revenue, much of which comes from state and local taxes.
Additionally, New York State is one of the most populous and economically diverse states in the country, with a wide range of services and infrastructure needs. The state government relies heavily on income tax revenue to fund these services, resulting in higher tax rates compared to many other states.
While high tax rates can be a burden for some residents, they also contribute to the city's vibrant economy and world-class amenities. Understanding the reasons behind these rates can help taxpayers appreciate the value they receive in return for their contributions.
Are NYC State Income Tax Rates Fair?
The fairness of NYC state income tax rates is a topic of ongoing debate. Proponents argue that the progressive tax system ensures that those who can afford to pay more do so, helping to fund essential services for all residents. Critics, however, contend that the high rates discourage economic growth and drive businesses and wealthy individuals to relocate to states with lower tax burdens.
Ultimately, the fairness of NYC state income tax rates depends on your perspective and financial situation. For many residents, the benefits of living in one of the world's greatest cities outweigh the costs, while others may seek more tax-friendly environments.
What Are the Deadlines for NYC State Income Tax Filing?
NYC state income tax filing deadlines typically align with federal tax deadlines, with April 15th being the standard deadline for most taxpayers. However, if April 15th falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline may be extended to the next business day. It's important to note that extensions for filing do not extend the deadline for paying any taxes owed, so taxpayers should plan accordingly.
Businesses and self-employed individuals may have different deadlines depending on their tax structure and filing requirements. For example, corporations must file their tax returns by the 15th day of the fourth month following the end of their tax year, while partnerships and S corporations have different deadlines.
To avoid penalties and interest, it's crucial to file your NYC state income tax returns on time and pay any taxes owed by the deadline. If you anticipate owing taxes but are unable to file by the deadline, you can request an extension to file, but you must still pay any estimated taxes owed by the original deadline.
Can You Request an Extension for NYC State Income Tax?
Yes, taxpayers can request an extension to file their NYC state income tax returns if they need additional time. This extension must be requested by the original filing deadline, and it grants an additional six months to file your return. However, the extension only applies to the filing deadline, not the payment deadline. Any taxes owed must still be paid by the original deadline to avoid penalties and interest.
How Does NYC State Income Tax Impact